Ehab and the Big Finale
题意翻译
这是一道交互题。
给你一棵 $n$ 个节点的有根树,$1$ 号点是根节点。
这棵树中有一个隐藏的节点 $x$,你需要通过询问把 $x$ 找出来。
你可以进行如下两种询问:
1. $d$ $u$ $(1\le u\le n)$。交互库会返回节点 $u$ 和 $x$ 的距离。
2. $s$ $u$ $(1\le u\le n)$。交互库会返回从 $u$ 到 $x$ 的路径上第二个点的标号。注意,在这类询问中,要求 $u$ 必须是 $x$ 的祖先。
你需要在不超过 $36$ 次询问之内找出 $x$。$x$ 是预先设定好的,不会随着询问而改变。
题目描述
This is an interactive problem.
You're given a tree consisting of $ n $ nodes, rooted at node $ 1 $ . A tree is a connected graph with no cycles.
We chose a hidden node $ x $ . In order to find this node, you can ask queries of two types:
- d $ u $ ( $ 1 \le u \le n $ ). We will answer with the distance between nodes $ u $ and $ x $ . The distance between two nodes is the number of edges in the shortest path between them.
- s $ u $ ( $ 1 \le u \le n $ ). We will answer with the second node on the path from $ u $ to $ x $ . However, there's a plot twist. If $ u $ is not an ancestor of $ x $ , you'll receive "Wrong answer" verdict!
Node $ a $ is called an ancestor of node $ b $ if $ a \ne b $ and the shortest path from node $ 1 $ to node $ b $ passes through node $ a $ . Note that in this problem a node is not an ancestor of itself.
Can you find $ x $ in no more than $ 36 $ queries? The hidden node is fixed in each test beforehand and does not depend on your queries.
输入输出格式
输入格式
The first line contains the integer $ n $ ( $ 2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ ) — the number of nodes in the tree.
Each of the next $ n-1 $ lines contains two space-separated integers $ u $ and $ v $ ( $ 1 \le u,v \le n $ ) that mean there's an edge between nodes $ u $ and $ v $ . It's guaranteed that the given graph is a tree.
输出格式
To print the answer, print "! x" (without quotes).
Interaction
To ask a question, print it in one of the formats above:
- d $ u $ ( $ 1 \le u \le n $ ), or
- s $ u $ ( $ 1 \le u \le n $ ).
After each question, you should read the answer: either the distance or the second vertex on the path, as mentioned in the legend.
If we answer with $ -1 $ instead of a valid answer, that means you exceeded the number of queries, made an invalid query, or violated the condition in the second type of queries. Exit immediately after receiving $ -1 $ and you will see Wrong answer verdict. Otherwise, you can get an arbitrary verdict because your solution will continue to read from a closed stream.
After printing a query, do not forget to output end of line and flush the output. Otherwise, you will get Idleness limit exceeded. To do this, use:
- fflush(stdout) or cout.flush() in C++;
- System.out.flush() in Java;
- flush(output) in Pascal;
- stdout.flush() in Python;
- See the documentation for other languages.
Hacks:
The first line should contain two integers $ n $ and $ x $ ( $ 2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ , $ 1 \le x \le n $ ).
Each of the next $ n-1 $ lines should contain two integers $ u $ and $ v $ ( $ 1 \le u,v \le n $ ) that mean there is an edge between nodes $ u $ and $ v $ . The edges must form a tree.
输入输出样例
输入样例 #1
5
1 2
1 3
3 4
3 5
3
5输出样例 #1
d 2
s 3
! 5说明
In the first example, the hidden node is node $ 5 $ .
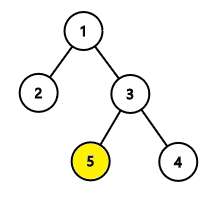We first ask about the distance between node $ x $ and node $ 2 $ . The answer is $ 3 $ , so node $ x $ is either $ 4 $ or $ 5 $ . We then ask about the second node in the path from node $ 3 $ to node $ x $ . Note here that node $ 3 $ is an ancestor of node $ 5 $ . We receive node $ 5 $ as the answer. Finally, we report that the hidden node is node $ 5 $ .