Something with XOR Queries
题意翻译
**这是一道交互题。(值得注意的是,这道题使用输入输出流而非函数接口实现交互)**
## 题目描述
Jury有一个$0\sim n-1$ 的排列$p$ ,你知道它的长度$n$ 。
定义另一个数列$b$ ,它与序列$p$ 互逆(即$\forall i,p_{b_i}=i$ )。
现在为了确定$p$ ,你每次可以询问一对$(i,j)$ ,并得到$p_i$ 与$b_j$ 的异或和。
可以证明即使你询问了所有$n^2$ 对数,仍可能有多个答案。
你需要在不超过$2n$ 次询问后回答$p$ 的可能数目,并给出一个合法解。
**同一组数据内$p$ 不随询问产生变化**
## 数据范围
$1\le n\le 5000$ 。
## 交互方式
首先你需要读入正整数$n$ 。
对于每个询问,你需要输出`? i j`表示这个询问,紧接着换行并清空输出流。在此之后读入一个数$x$ 表示询问结果。
如果程序运行中你读入到了一个数$-1$ ,表明你做出了超过$2n$ 次询问或询问不合法,请**立即退出**,评测结果将会是`Wrong Answer`。
当你要递交答案时,先输出一行一个`!`,接下来输出一行一个数表示合法方案数,第三行输出$n$ 个数表示一个合法的排列$p$ 。
### 清空输出流方法
在输出后调用下列语句:
- fflush(stdout) in C++
- System.out.flush() in Java
- stdout.flush() in Python
- flush(output) in Pascal
题目描述
This is an interactive problem.
Jury has hidden a permutation $ p $ of integers from $ 0 $ to $ n-1 $ . You know only the length $ n $ . Remind that in permutation all integers are distinct.
Let $ b $ be the inverse permutation for $ p $ , i.e. $ p_{bi}=i $ for all $ i $ . The only thing you can do is to ask xor of elements $ p_{i} $ and $ b_{j} $ , printing two indices $ i $ and $ j $ (not necessarily distinct). As a result of the query with indices $ i $ and $ j $ you'll get the value , where  denotes the xor operation. You can find the description of xor operation in notes.
Note that some permutations can remain indistinguishable from the hidden one, even if you make all possible $ n^{2} $ queries. You have to compute the number of permutations indistinguishable from the hidden one, and print one of such permutations, making no more than $ 2n $ queries.
The hidden permutation does not depend on your queries.
输入输出格式
输入格式
The first line contains single integer $ n $ ( $ 1<=n<=5000 $ ) — the length of the hidden permutation. You should read this integer first.
输出格式
When your program is ready to print the answer, print three lines.
In the first line print "!".
In the second line print single integer $ answers_cnt $ — the number of permutations indistinguishable from the hidden one, including the hidden one.
In the third line print $ n $ integers $ p_{0},p_{1},...,p_{n-1} $ ( $ 0<=p_{i}<n $ , all $ p_{i} $ should be distinct) — one of the permutations indistinguishable from the hidden one.
Your program should terminate after printing the answer.
Interaction
To ask about xor of two elements, print a string "? i j", where $ i $ and $ j $ — are integers from $ 0 $ to $ n-1 $ — the index of the permutation element and the index of the inverse permutation element you want to know the xor-sum for. After that print a line break and make flush operation.
After printing the query your program should read single integer — the value of .
For a permutation of length $ n $ your program should make no more than $ 2n $ queries about xor-sum. Note that printing answer doesn't count as a query. Note that you can't ask more than $ 2n $ questions. If you ask more than $ 2n $ questions or at least one incorrect question, your solution will get "Wrong answer".
If at some moment your program reads -1 as an answer, it should immediately exit (for example, by calling exit(0)). You will get "Wrong answer" in this case, it means that you asked more than $ 2n $ questions, or asked an invalid question. If you ignore this, you can get other verdicts since your program will continue to read from a closed stream.
Your solution will get "Idleness Limit Exceeded", if you don't print anything or forget to flush the output, including for the final answer .
To flush you can use (just after printing line break):
- fflush(stdout) in C++;
- System.out.flush() in Java;
- stdout.flush() in Python;
- flush(output) in Pascal;
- For other languages see the documentation.
Hacking
For hacking use the following format:
$ n $
$ p_{0} $ $ p_{1} $ ... $ p_{n-1} $
Contestant programs will not be able to see this input.
输入输出样例
输入样例 #1
3
0
0
3
2
3
2输出样例 #1
? 0 0
? 1 1
? 1 2
? 0 2
? 2 1
? 2 0
!
1
0 1 2输入样例 #2
4
2
3
2
0
2
3
2
0输出样例 #2
? 0 1
? 1 2
? 2 3
? 3 3
? 3 2
? 2 1
? 1 0
? 0 0
!
2
3 1 2 0说明
xor operation, or bitwise exclusive OR, is an operation performed over two integers, in which the $ i $ -th digit in binary representation of the result is equal to $ 1 $ if and only if exactly one of the two integers has the $ i $ -th digit in binary representation equal to $ 1 $ . For more information, see [here](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bitwise_operation#XOR).
In the first example $ p=[0,1,2] $ , thus $ b=[0,1,2] $ , the values  are correct for the given $ i,j $ . There are no other permutations that give the same answers for the given queries.
The answers for the queries are:
- 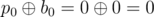,
- 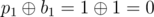,
- 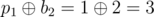,
- 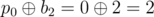,
- 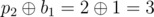,
- 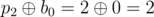.
In the second example $ p=[3,1,2,0] $ , and $ b=[3,1,2,0] $ , the values  match for all pairs $ i,j $ . But there is one more suitable permutation $ p=[0,2,1,3] $ , $ b=[0,2,1,3] $ that matches all $ n^{2} $ possible queries as well. All other permutations do not match even the shown queries.