Winning Strategy
题意翻译
某比赛每年举办一次,某校有无穷多的学生作为参赛的后备力量。每个学生最多可以参加两次比赛。该校每次比赛最多可派出$n$名学生参赛,而且获胜的概率与$n$名学生中第二次参赛的学生人数正相关。具体来说,如果有$i$人参赛,那么胜率为$p_i$,保证$\forall i\in[1,n],p_{i-1}\le p_i$。
请安排一种策略,最大化该校获胜的平均概率。
形式化的,请找到一个合法的无穷序列$\{a_i\}$表示第$i$次比赛派出的第二次参赛的学生人数,最大化$\lim\limits_{m\rightarrow\infty}\frac{\sum_{i=1}^m p_{a_i}}{m}$并输出这个值。
题目描述
One university has just found out about a sport programming contest called ACM ICPC v2.0. This contest doesn't differ much from the well-known ACM ICPC, for example, the participants are not allowed to take part in the finals more than two times. However, there is one notable difference: the teams in the contest should consist of exactly $ n $ participants.
Having taken part in several ACM ICPC v2.0 finals and having not won any medals, the students and the university governors realized that it's high time they changed something about the preparation process. Specifically, as the first innovation it was decided to change the teams' formation process. Having spent considerable amount of time on studying the statistics of other universities' performance, they managed to receive some interesting information: the dependence between the probability of winning a medal and the number of team members that participated in the finals in the past. More formally, we know $ n+1 $ real numbers $ p_{0}<=p_{1}<=...<=p_{n} $ , where $ p_{i} $ is the probability of getting a medal on the finals if the team has $ i $ participants of previous finals, and other $ n-i $ participants arrived to the finals for the first time.
Despite such useful data, the university governors are unable to determine such team forming tactics that would provide the maximum probability of winning a medal at ACM ICPC v2.0 finals on average (we are supposed to want to provide such result to the far future and we are also supposed to have an endless supply of students). And how about you, can you offer such optimal tactic? At the first stage the university governors want to know the value of maximum average probability.
More formally, suppose that the university sends a team to the $ k $ -th world finals. The team has $ a_{k} $ participants of previous finals ( $ 0<=a_{k}<=n $ ). Since each person can participate in the finals no more than twice, the following condition must be true: 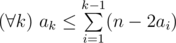. Your task is to choose sequence 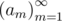 so that the limit $ Ψ $ exists and it's value is maximal:
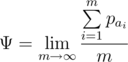As 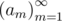 is an infinite sequence, you should only print the maximum value of the $ Ψ $ limit.
输入输出格式
输入格式
The first line contains an integer $ n $ ( $ 3<=n<=100 $ ), $ n $ is the number of team participants. The second line contains $ n+1 $ real numbers with no more than 6 digits after decimal point $ p_{i} $ ( $ 0<=i<=n,0<=p_{i}<=1 $ ) — the probability of that the team will win a medal if it contains $ i $ participants who has already been on the finals. Also the condition $ p_{i}<=p_{i+1} $ should be fulfilled for all $ 0<=i<=n-1 $ .
输出格式
Print the only real number — the expected average number of medals won per year if the optimal strategy is used. The result may have absolute or relative error $ 10^{-6} $ .
输入输出样例
输入样例 #1
3
0.115590 0.384031 0.443128 0.562356
输出样例 #1
0.4286122500
输入样例 #2
3
1 1 1 1
输出样例 #2
0.9999999999
说明
In the second test, no matter what participants the team contains, it is doomed to be successful.